Leak testing of gas pipelines:
Playing it safe when it comes to measurement
New or modified pipeline? Following assembly, it must then undergo load testing and leak testing according to DVGW-TRGI 2018. In the first step, serviceability testing is carried out. This is followed by leak testing.
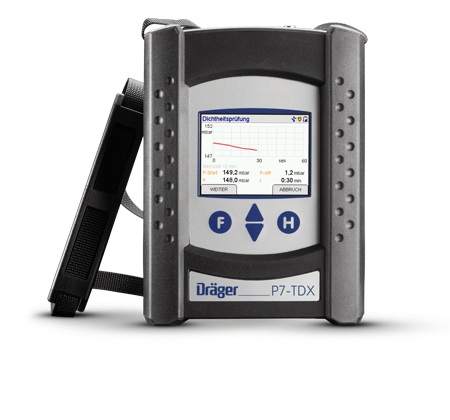
For leak testing of gas pipelines, a pressure and leak testing device is required that goes up to a minimal resolution of 0.1 bar. With the Dräger P7-TD and the Dräger P7-TDX you can carry out leak testing of gas pipelines with the flick of a wrist.
How is the leak testing of gas pipelines carried out safely?
Leak testing of gas pipelines is done including the fittings, but without a gas device and the associated regulating and safety fittings. The gas pipelines must be closed with a suitable seal. At the meter position, the single-tube meter cover is used directly for testing for leaks.
In dual-tube meters, a corset is screwed between the single-tube meter cap and the dual-tube gas connection. The test pressure is achieved via the pump in the pressure measurement device. After the gas pipeline is filled with 150 mbar or inert gas, the temperature balance must be awaited according to this table:
Leak testing 5.6.4.2, stabilisation and testing times (DVGW TRGI 2018, Worksheet G600)
| Pipeline volume | Adjustment time | mind. Test duration |
|---|---|---|
| < 100 l | 10 min | 10 min |
| < 200 l | 30 min | 20 min |
| ≥ 200 l | 60 min | 30 min |
Leak testing is carried out before the intake of gases, before cladding and after load testing with 1 or 3 bar, with 150 mbar air or inert gas at different time intervals. During the test period, the test pressure must not drop. Then, the leak testing of gas pipelines begins automatically. All current values are then shown in the display of the measurement device.
If the end pressure does not deviate from the set starting pressure, the prescribed duration of measurement is adhered to, and no pressure drop occurs, you can be sure the gas pipelines are leakproof. After the testing of gas pipelines for leaks, with a printout from the printer you receive an overview of all the measured values. We also recommend preparing a measurement report for documentation via a PC.
The leak testing of gas pipelines is carried out in the sanitary, heating, and air conditioning industry, by heating engineers, installers and in industry and utility companies.
Questions on testing gas and water pipelines
Few industries have such high safety standards as the gas industry. The guidelines and specifications of the DVGW are accordingly stringent and call for regular inspection and control. For drinking water systems, leakproof status and hygiene must be guaranteed.
TRGI stands for the ‘Technical Regulation for Gas Installation’ (Technische Regel für Gasinstallation) and is the most important datasheet for gas installations in buildings. It contains regulations for planning, production, modification and operation of gas installations with an operating pressure of up to 1 bar in buildings and on property. Significant content for measurement technology Chapter V and Section 13 includes three different tests (lines up to 100 mbar operating pressure):
- Load test (pre-test)
- Leak detection (main testing)
- Serviceability testing (leak rate measurement)
Serviceability testing is required every 12 years for operating pipeline systems with operating pressures of up to 100 mbar. Additionally, an annual visual inspection must be carried out of the pipeline system on wall ducts.
TRF stands for ‘Technical Regulations for Liquefied Gas’ in German, comprising rules and requirements for the marketing, establishment and operation of liquefied gas systems based on applicable regulations and standards. The TRF establishes a pressure test and leak test that must be carried out immediately before commissioning. Then, a recurring leak test for lines that are in operation is prescribed.
The DIN 806-4 is a European standard that regulates the testing of drinking water systems. It contains recommendations and requirements for the installation of drinking water systems inside buildings and the installation of pipelines outside buildings. It can be used on new installations, overhauls and repairs.
The ZVSHK datasheet focuses on leak detection of drinking water systems with compressed air, inert gas or water. There are three variants for leak detection with water, depending on the active ingredient. The modified method can be used for all substances and combinations of substances. For leak detection with water, test method B as per DIN EN 806-4 applies. The test time is extended according to the current datasheet so that even the smallest leaks can be detected during the leak test. Additionally, the duration of the test method is expanded with compressed air or inert gases.
DIN EN 1610 is the basic standard for the installation and testing of sewage pipelines and tunnels. In the testing of sewage pipelines with air, the test duration depends on the test method, the substance and the pipe diameter.
Worksheet G 459/I addresses the planning and design of house connections for gas supply up to 4 bar operating pressure. Pressure testing must be carried out before commissioning according to DVGW Worksheet G 469.
Pressure testing for house connection pipelines can be carried out with the Dräger P7-TS.