Leak detection in sewage pipelines:
Absolute safety in only a few steps
Leak detection in sewage pipelines according to DIN EN 1610 applies to new and refurbished sewage pipelines and tunnels in buildings. This requires dependable measurements - because a leak can result in contamination of the groundwater and soil, resulting in the spread of disease.
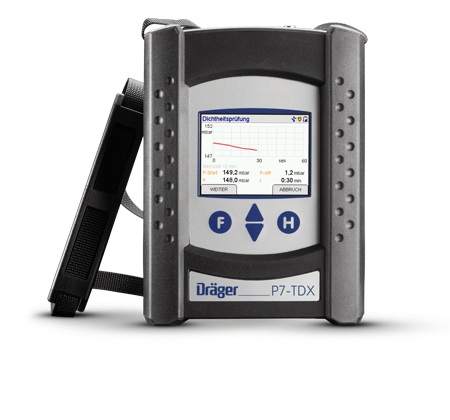
The best measurement instrument for sewage leak testing is the Dräger P7-TDX.
How is leak detection in sewage pipelines carried out safely?
For sewage leak detection using air (method L), the initial pressure, which exceeds the required test pressure by approx. 10%, must be initially maintained for a few minutes. After that, the test pressure must be set according to test method LC (100 mbar) or LD (200 mbar). If the drop in pressure measured after the test time is lower than 15 mbar for both these test methods, the pipeline complies with requirements.
In leak detection in sewage pipelines, the sewage pipeline to be tested is connected with a pressure hose via a pneumatic fast coupling to the pressure inlet of the measurement device. And sewage pipeline testing begins. The test pressure is first increased 1.1-fold. Next comes the stabilisation phase.
After the stabilisation phase, the pressure is reduced to test pressure. Now, the actual testing time begins. If during leak detection in sewage pipelines a pressure loss over 15 mbar is determined, this indicates a leak.
The following materials and test methods can be selected:
- Concrete dry cast LC 100 mbar = dry cast concrete pipes
Test method LC (100 mbar) - Concrete dry cast LD 200 mbar = dry cast concrete pipes
Test method LD (200 mbar) - Concrete wet cast LC 100 mbar =wet cast concrete pipes and all other materials
- Test method LC (100 mbar)
- Concrete wet cast LD 200 mbar = wet cast concrete pipes and all other materials
- Test method LD (200 mbar)
Sewage pipeline leak testing is carried out by sanitary, heating, and air conditioning professionals, by pipe remediators, installers, and in industry and municipal utilities.
TRGI stands for the ‘Technical Regulation for Gas Installation’ (Technische Regel für Gasinstallation) and is the most important datasheet for gas installations in buildings. It contains regulations for planning, production, modification and operation of gas installations with an operating pressure of up to 1 bar in buildings and on property. Significant content for measurement technology Chapter V and Section 13 includes three different tests (lines up to 100 mbar operating pressure):
- Load test (pre-test)
- Leak detection (main testing)
- Serviceability testing (leak rate measurement)
Serviceability testing is required every 12 years for operating pipeline systems with operating pressures of up to 100 mbar. Additionally, an annual visual inspection must be carried out of the pipeline system on wall ducts.
TRF stands for ‘Technical Regulations for Liquefied Gas’ in German, comprising rules and requirements for the marketing, establishment and operation of liquefied gas systems based on applicable regulations and standards. The TRF establishes a pressure test and leak test that must be carried out immediately before commissioning. Then, a recurring leak test for lines that are in operation is prescribed.
The DIN 806-4 is a European standard that regulates the testing of drinking water systems. It contains recommendations and requirements for the installation of drinking water systems inside buildings and the installation of pipelines outside buildings. It can be used on new installations, overhauls and repairs.
The ZVSHK datasheet focuses on leak detection of drinking water systems with compressed air, inert gas or water. There are three variants for leak detection with water, depending on the active ingredient. The modified method can be used for all substances and combinations of substances. For leak detection with water, test method B as per DIN EN 806-4 applies. The test time is extended according to the current datasheet so that even the smallest leaks can be detected during the leak test. Additionally, the duration of the test method is expanded with compressed air or inert gases.
DIN EN 1610 is the basic standard for the installation and testing of sewage pipelines and tunnels. In the testing of sewage pipelines with air, the test duration depends on the test method, the substance and the pipe diameter.
Worksheet G 459/I addresses the planning and design of house connections for gas supply up to 4 bar operating pressure. Pressure testing must be carried out before commissioning according to DVGW Worksheet G 469.
Pressure testing for house connection pipelines can be carried out with the Dräger P7-TD or the Dräger P7-TDX.